energy harvesting rfid tag Energy harvesting for wireless sensors and RFID smart tags is a critical design feature on the path to the grand vision of ubiquitous computing. An important subset of energy harvesting solutions is the use of the RF reader signal to . It doesn't let you emulate amiibos, it let's the system use them. The o3ds doesn't have a NFC .
0 · Field Focusing for Energy Harvesting Applications in Smart RFID
1 · Energy Harvesting in RFID Systems
2 · A Comprehensive Survey on RF Energy Harvesting:
$26.99
The proposed approach is, in principle, able to maximize the energy transfer as it aims at confining the RF power on the considered RFID device. Moreover, being the approach based . At the end of this paper, an energy harvesting model is proposed to incorporate this simplest of concepts, implementing the basic electromagnetic inductance characteristics of an RFID passive tag where energy is induced in a tag from .The proposed approach is, in principle, able to maximize the energy transfer as it aims at confining the RF power on the considered RFID device. Moreover, being the approach based on a real-time procedure, it is able to deal with moving RFID tag embedded into an unknown scenario.
clear nfc tags
The electromagnetic energy harvesting for smart RFID sensors in a WSN is then a critical design feature on the path to the grand vision of ubiquitous computing. The literature defines this smart tag embodiment as the Wireless Identification and Sensing Platform (WISP) [36]. Energy harvesting for wireless sensors and RFID smart tags is a critical design feature on the path to the grand vision of ubiquitous computing. An important subset of energy harvesting solutions is the use of the RF reader signal to .
The need and dynamics of RF power harvesting for active RFID tags are identified and highlighted. In Ref. , RF energy harvesting is identified as a source of green energy, suitable for a range of sensor applications in harsh environments. Moreover, this work proposes a T-matched meandered line antenna (MLA) and a folded dipole antenna for RFID tag interrogation and RF energy harvesting, respectively. A novel sensing data management structure which is compatible with the EPCglobal Class 1 Generation 2 standard is also proposed.Aiming to blend the advantages of passive and active RFID tags, this work presents the operation of a battery-free hybrid RFID tag possessing autonomous capabil.
This paper presents an energy-autonomous antenna system that combines energy harvesting (EH) with radio frequency identification (RFID) communication to measure the battery charge level in real. By capturing radio wave energy for passive RFID tags, RFID energy harvesting provides an economical and environmentally friendly alternative to batteries for low-power applications. The objectives of the project include designing an effective RF energy harvester, building a power management circuit, and thoroughly testing the device.
In this study, a dual-mode UHF RFID tag is proposed. The PV and TE energy-harvesting topology is adopted along with RF energy harvesting to eliminate the external battery. The reconfigurable architecture of the receiver is introduced to be compatible with conventional passive RFID tags. At the end of this paper, an energy harvesting model is proposed to incorporate this simplest of concepts, implementing the basic electromagnetic inductance characteristics of an RFID passive tag where energy is induced in a tag from .The proposed approach is, in principle, able to maximize the energy transfer as it aims at confining the RF power on the considered RFID device. Moreover, being the approach based on a real-time procedure, it is able to deal with moving RFID tag embedded into an unknown scenario.The electromagnetic energy harvesting for smart RFID sensors in a WSN is then a critical design feature on the path to the grand vision of ubiquitous computing. The literature defines this smart tag embodiment as the Wireless Identification and Sensing Platform (WISP) [36].
Energy harvesting for wireless sensors and RFID smart tags is a critical design feature on the path to the grand vision of ubiquitous computing. An important subset of energy harvesting solutions is the use of the RF reader signal to . The need and dynamics of RF power harvesting for active RFID tags are identified and highlighted. In Ref. , RF energy harvesting is identified as a source of green energy, suitable for a range of sensor applications in harsh environments.
Moreover, this work proposes a T-matched meandered line antenna (MLA) and a folded dipole antenna for RFID tag interrogation and RF energy harvesting, respectively. A novel sensing data management structure which is compatible with the EPCglobal Class 1 Generation 2 standard is also proposed.
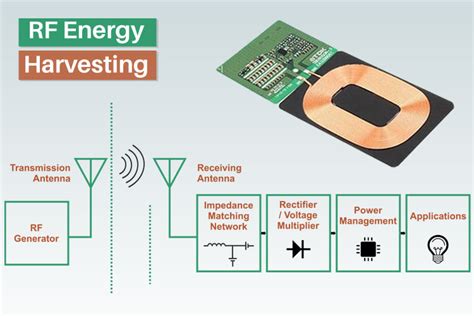
Aiming to blend the advantages of passive and active RFID tags, this work presents the operation of a battery-free hybrid RFID tag possessing autonomous capabil. This paper presents an energy-autonomous antenna system that combines energy harvesting (EH) with radio frequency identification (RFID) communication to measure the battery charge level in real. By capturing radio wave energy for passive RFID tags, RFID energy harvesting provides an economical and environmentally friendly alternative to batteries for low-power applications. The objectives of the project include designing an effective RF energy harvester, building a power management circuit, and thoroughly testing the device.
Field Focusing for Energy Harvesting Applications in Smart RFID
Scan this QR code to download the app now. Or check it out in the app stores
energy harvesting rfid tag|Energy Harvesting in RFID Systems