wifi rfid reader-iot application In this paper, a spider web-shaped ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID reader . Sunday, December 29, 1985. 1985 NFC Wild Card Game; Sun 12/29 1 2 3 4 FINAL; San Francisco (10-6): 0: Pass
0 · what is rfid reader
1 · what is rfid
2 · rfid technology
3 · rfid sensors iot
4 · rfid sensor technology
5 · mdpi rfid sensor
6 · ieee xplore rfid
7 · ieee rfid sensors
AFC Miami Dolphins (9-3) Baltimore Ravens (9-3) Kansas City Chiefs (8-4) See more
In this paper, a spider web-shaped ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID reader .

Applications. Applications for IoT-enabled RFID readers are vast, encompassing sectors such . In this paper, a spider web-shaped ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID reader antenna-based system for the Internet of Things (IoT) and healthcare applications is proposed.
Applications. Applications for IoT-enabled RFID readers are vast, encompassing sectors such as retail, logistics, healthcare, and asset management. In retail, these smart RFID systems help businesses optimize inventory control and enhance customer experience through accurate stock .
A RFID reader is powered by a battery or from an external power source, and generates an interrogation signal centered at the specific operating frequency. The signal is then emitted by the RFID reader antenna after an electrical-to-electromagnetic conversion. Radio-Frequency IDentification (RFID) devices and sensors are among the main innovations of the last years, with an enormous impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) physical communication layer as well as on logistics and robotics.HF and UHF RFID Technologies. Wireless communication between reader and batteryless/passive tags (antenna and chip) § Reader–tag: RF power and data § Tag–reader (no transmitter): reader signal modulated/reflected by tag (tag ID) § Operating frequency/wavelength: 13.56 MHz / 22.1 m (HF), 868 MHz / 30 cm (UHF )
Connecting RFID reader to the terminal of Internet, the readers can identify, track and monitor the objects attached with tags globally, automatically, and in real time, if needed. This is the so-called Internet of Things (IoT). RFID Readers. RFID transceivers can both receive information from the tag and transmit this information onwards to application software. The reader may also be able to communicate bi-directionally, transferring information from the application to the tag. It is usually comprised of a radio frequency interface (RFI) module and control unit. RFID . Passive RFID sensors harvest the RF energy from RF radiation to power the circuit, perform the sensing task, and save the data in the RFID chip to be accessed by RFID readers. Both analog and digital RFID sensing can provide a variety of .
A Batteryless Six-Port RFID-Based Wireless Sensor Architecture for IoT Applications. Publisher: IEEE. Cite This. PDF. Nabil Khalid; Ashwin K. Iyer; Rashid Mirzavand. All Authors. 6. Cites in. Papers. 616. Full. Text Views.A review of technological solutions for RFID sensing and their current or envisioned applications is presented. The fundamentals of the wireless sensing technology are summarized in the first part of the work, and the benefits of adopting RFID sensors for replacing standard sensor-equipped Wi-Fi nodes are discussed. In this paper, a spider web-shaped ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID reader antenna-based system for the Internet of Things (IoT) and healthcare applications is proposed.Applications. Applications for IoT-enabled RFID readers are vast, encompassing sectors such as retail, logistics, healthcare, and asset management. In retail, these smart RFID systems help businesses optimize inventory control and enhance customer experience through accurate stock .
A RFID reader is powered by a battery or from an external power source, and generates an interrogation signal centered at the specific operating frequency. The signal is then emitted by the RFID reader antenna after an electrical-to-electromagnetic conversion. Radio-Frequency IDentification (RFID) devices and sensors are among the main innovations of the last years, with an enormous impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) physical communication layer as well as on logistics and robotics.
what is rfid reader
HF and UHF RFID Technologies. Wireless communication between reader and batteryless/passive tags (antenna and chip) § Reader–tag: RF power and data § Tag–reader (no transmitter): reader signal modulated/reflected by tag (tag ID) § Operating frequency/wavelength: 13.56 MHz / 22.1 m (HF), 868 MHz / 30 cm (UHF ) Connecting RFID reader to the terminal of Internet, the readers can identify, track and monitor the objects attached with tags globally, automatically, and in real time, if needed. This is the so-called Internet of Things (IoT). RFID Readers. RFID transceivers can both receive information from the tag and transmit this information onwards to application software. The reader may also be able to communicate bi-directionally, transferring information from the application to the tag. It is usually comprised of a radio frequency interface (RFI) module and control unit. RFID . Passive RFID sensors harvest the RF energy from RF radiation to power the circuit, perform the sensing task, and save the data in the RFID chip to be accessed by RFID readers. Both analog and digital RFID sensing can provide a variety of .
transportation smart card beijing
A Batteryless Six-Port RFID-Based Wireless Sensor Architecture for IoT Applications. Publisher: IEEE. Cite This. PDF. Nabil Khalid; Ashwin K. Iyer; Rashid Mirzavand. All Authors. 6. Cites in. Papers. 616. Full. Text Views.
tama smart card
what is rfid
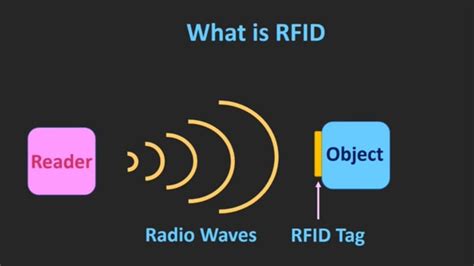
rfid technology

These cards use Near Field Communications (NFC) technology, enabling customers to make payment at payment terminals without swiping it. Just placing it over the .
wifi rfid reader-iot application|ieee rfid sensors