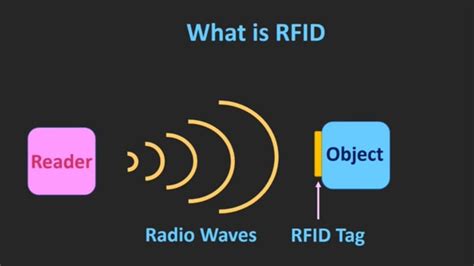
static identifier chip silent mode rfid Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive equipment more quickly to improve patient care, pharmaceutical companies to reduce counterfeiting and logistics providers to improve the management of moveable assets.
The affiliates list also includes the renewal of stations in major markets of .
0 · what is rfid
1 · rfid white paper
2 · rfid bar code
Stream NCAA Radio - Auburn Tigers at South Carolina Gamecocks on January 11, 2025 12:00 am. Listen to play-by-play of every NCAA game on TuneIn Radio. . Auburn Tigers at South .
what is rfid
pt200 rfid handheld reader from china supplier
Early transit cards supported static unique identifiers (UIDs) of 4 bytes in length. These worked well until adoption grew so much that reproduced cards were often encountered. NFC chip makers upgraded to universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) of 7 bytes to address this . Ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification (UHF RFID) systems have been widely adopted for applications like asset management and apparel retail. Recently, they have .Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive . Early transit cards supported static unique identifiers (UIDs) of 4 bytes in length. These worked well until adoption grew so much that reproduced cards were often encountered. NFC chip makers upgraded to universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) of .
Ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification (UHF RFID) systems have been widely adopted for applications like asset management and apparel retail. Recently, they have gained attention for use in unmanned supermarket applications and for the electronic identification of motor vehicles.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive equipment more quickly to improve patient care, pharmaceutical companies to reduce counterfeiting and logistics providers to improve the management of moveable assets.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems use radio frequency to identify, locate and track people, assets, and animals. Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer. Recommendations: For use cases with a static tag population, take advantage of Mode 1002 with its high unique tag reads. If the reader is operating in a noisy RF Environment, select a slower (Dense Reader) mode. application might only need a unique static identifier value for each tagged object, while others may need to store additional sensitive information about each tagged object over time. The physical and technical environment should also be considered at the time an NFC/RFID tap occurs, but also
RFID provides a non-contact way of collecting information about a product or device. In general, the transponders (or "tags") cost little – often under a dollar – and can therefore be more or less disposable. Libraries use tags to track individual books.
An RFID chip is typically a simple piece of hardware with a unique identifier and a small amount of read/write storage. Currently, this storage is insufficient for significant medical information, so the chip usually stores only a patient identifier, which links to a complete electronic record stored separately.The "silent mode" is considered as an alternative to kill the tag. In this mode, the RFID tag can be shut off instead of killing it at the time the customer purchases an item. This mode maintains all the information that could be utilized further in case of reclamation situations. We present a brief history of RFID technology and automatic identification systems. We summarize major RFID applications, and present a primer on RFID fundamental principles. Finally, we discuss several challenges and obstacles to RFID adoption, as well as emerging technologies relevant to RFID.
rfid white paper
Early transit cards supported static unique identifiers (UIDs) of 4 bytes in length. These worked well until adoption grew so much that reproduced cards were often encountered. NFC chip makers upgraded to universally unique identifiers (UUIDs) of . Ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification (UHF RFID) systems have been widely adopted for applications like asset management and apparel retail. Recently, they have gained attention for use in unmanned supermarket applications and for the electronic identification of motor vehicles.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is evolving as a major technology enabler for identifying and tracking goods and assets around the world. It can help hospitals locate expensive equipment more quickly to improve patient care, pharmaceutical companies to reduce counterfeiting and logistics providers to improve the management of moveable assets.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems use radio frequency to identify, locate and track people, assets, and animals. Passive RFID systems are composed of three components – an interrogator (reader), a passive tag, and a host computer.
Recommendations: For use cases with a static tag population, take advantage of Mode 1002 with its high unique tag reads. If the reader is operating in a noisy RF Environment, select a slower (Dense Reader) mode.
application might only need a unique static identifier value for each tagged object, while others may need to store additional sensitive information about each tagged object over time. The physical and technical environment should also be considered at the time an NFC/RFID tap occurs, but also RFID provides a non-contact way of collecting information about a product or device. In general, the transponders (or "tags") cost little – often under a dollar – and can therefore be more or less disposable. Libraries use tags to track individual books.
An RFID chip is typically a simple piece of hardware with a unique identifier and a small amount of read/write storage. Currently, this storage is insufficient for significant medical information, so the chip usually stores only a patient identifier, which links to a complete electronic record stored separately.The "silent mode" is considered as an alternative to kill the tag. In this mode, the RFID tag can be shut off instead of killing it at the time the customer purchases an item. This mode maintains all the information that could be utilized further in case of reclamation situations.

Communications. Hybrid SIM slot, nano-SIM + nano-SIM or microSD. Up to 256GB expandable storage. Supports dual SIM and dual VoLTE. Note: Dual VoLTE requires the support of local telecom operator services, and may not .
static identifier chip silent mode rfid|rfid white paper