examples of smart card and magnetic stripe card A magnetic stripe card, often referred to as a magstripe card, is a type of card that stores data via a magnetic stripe on its back. This stripe is embedded with iron-based magnetic particles and is used to store user-specific information. Find great deals on eBay for Nintendo 3DS Nfc Reader Writer for. Shop with confidence. Skip .$24.99
0 · who invented magnetic Stripe card
1 · types of magnetic Stripe cards
2 · magnetic Stripe card vs chip card
3 · magnetic Stripe card size
4 · magnetic Stripe card definition
5 · magnetic Stripe card decoder
6 · magnetic Stripe card credit card
7 · advantages of magnetic Stripe card
The New Nintendo 3DS XL comes with built-in amiibo support. Just tap an amiibo to the NFC reader on the lower screen and go. You can also use amiibo with .I have uploaded every Amiibo .Bin and .NFC file I could get my hands on. I have NOT tested all of these but I have tested most, so please let . See more
Types of magnetic stripe cards currently in use include credit and debit cards, some driver's licenses, employee ID cards, hotel room "keys," gift cards, and public transit cards. Magnetic.A magnetic stripe card, often referred to as a magstripe card, is a type of card that stores data via a magnetic stripe on its back. This stripe is embedded with iron-based magnetic particles and is used to store user-specific information.Smart cards are now ubiquitous and have largely replaced magnetic stripe -- also known as mag stripe -- card technology, which only has a capacity of 300 bytes of nonrewriteable memory and no processing capability. How smart cards work.A magnetic stripe card contains a magnetic stripe that stores information. Unlike smart cards, magnetic stripe cards are passive devices that contain no circuits. These cards are sometimes called swipe cards, as they are used by swiping them through a card reader.
Smart cards are credit or debit cards that contain an embedded microprocessor chip. These microprocessors are able to store and process data directly. Unlike traditional magnetic stripe cards, they don’t require a remote connection. This chapter provides a first introduction to a wide range of smart cards and tokens, considering the various types, capabilities, popular applications and the practicality of their development and deployment, covered in detail within .
Bank cards, transportation cards, and ID cards are all common smart cards in our lives. It usually consists of a microprocessor, memory (such as EEPROM or Flash), and a contact or contactless interface. Smart cards perform complex .

As more and more organizations and individuals transition away from magnetic stripe cards, it is critical to take a closer look at the merits of their alternative: the smart card. Here, learn about the advantages of smart cards -- .What are the types of smart cards? To begin with, magnetic stripe cards are definitively not smart cards. Memory vs microprocessor. Smart cards come in two varieties: memory and microprocessor (smart chip). Memory cards store data and can be viewed as small USB memory sticks with optional security. Types of magnetic stripe cards currently in use include credit and debit cards, some driver's licenses, employee ID cards, hotel room "keys," gift cards, and public transit cards. Magnetic.
A magnetic stripe card, often referred to as a magstripe card, is a type of card that stores data via a magnetic stripe on its back. This stripe is embedded with iron-based magnetic particles and is used to store user-specific information.Smart cards are now ubiquitous and have largely replaced magnetic stripe -- also known as mag stripe -- card technology, which only has a capacity of 300 bytes of nonrewriteable memory and no processing capability. How smart cards work.A magnetic stripe card contains a magnetic stripe that stores information. Unlike smart cards, magnetic stripe cards are passive devices that contain no circuits. These cards are sometimes called swipe cards, as they are used by swiping them through a card reader.
Smart cards are credit or debit cards that contain an embedded microprocessor chip. These microprocessors are able to store and process data directly. Unlike traditional magnetic stripe cards, they don’t require a remote connection. This chapter provides a first introduction to a wide range of smart cards and tokens, considering the various types, capabilities, popular applications and the practicality of their development and deployment, covered in detail within .

Bank cards, transportation cards, and ID cards are all common smart cards in our lives. It usually consists of a microprocessor, memory (such as EEPROM or Flash), and a contact or contactless interface. Smart cards perform complex data processing and encryption operations.
As more and more organizations and individuals transition away from magnetic stripe cards, it is critical to take a closer look at the merits of their alternative: the smart card. Here, learn about the advantages of smart cards -- and a few potential disadvantages, too.What are the types of smart cards? To begin with, magnetic stripe cards are definitively not smart cards. Memory vs microprocessor. Smart cards come in two varieties: memory and microprocessor (smart chip). Memory cards store data and can be viewed as small USB memory sticks with optional security.
who invented magnetic Stripe card
Types of magnetic stripe cards currently in use include credit and debit cards, some driver's licenses, employee ID cards, hotel room "keys," gift cards, and public transit cards. Magnetic.
A magnetic stripe card, often referred to as a magstripe card, is a type of card that stores data via a magnetic stripe on its back. This stripe is embedded with iron-based magnetic particles and is used to store user-specific information.Smart cards are now ubiquitous and have largely replaced magnetic stripe -- also known as mag stripe -- card technology, which only has a capacity of 300 bytes of nonrewriteable memory and no processing capability. How smart cards work.A magnetic stripe card contains a magnetic stripe that stores information. Unlike smart cards, magnetic stripe cards are passive devices that contain no circuits. These cards are sometimes called swipe cards, as they are used by swiping them through a card reader.
Smart cards are credit or debit cards that contain an embedded microprocessor chip. These microprocessors are able to store and process data directly. Unlike traditional magnetic stripe cards, they don’t require a remote connection.
This chapter provides a first introduction to a wide range of smart cards and tokens, considering the various types, capabilities, popular applications and the practicality of their development and deployment, covered in detail within .Bank cards, transportation cards, and ID cards are all common smart cards in our lives. It usually consists of a microprocessor, memory (such as EEPROM or Flash), and a contact or contactless interface. Smart cards perform complex data processing and encryption operations.
types of magnetic Stripe cards
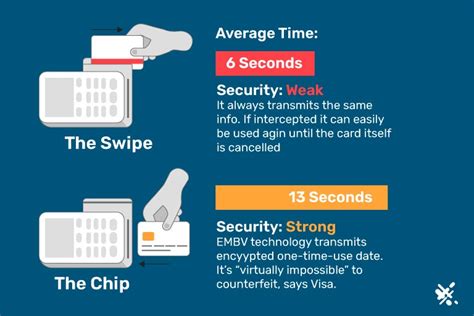
More recently, NFC has incorporated the ISO 15693 standard, which offers a maximum read range of about 3 feet. So it would make sense to use ISO 15693 tags, rather than NFC tags based on ISO 14443. It is possible to increase the .
examples of smart card and magnetic stripe card|magnetic Stripe card vs chip card