what is a semi active rfid Semi-passive RFID tags look more like passive tags in terms of size and ease of manufacture. but like active tags, they incorporate a power source—usually a small, eco-friendlier battery—to improve data transmission.
Nuclear Fuel Complex, ECIL Post, Hyderabad – 500 062 SCHEDULE OF LEVEL-II EXAMINATION FOR THE POST OF UPPER DIVISION CLERK AGAINST ADVT. .
0 · RFID and the Differences in Passive, Semi
1 · Passive RFID versus Active RFID
2 · How to Make Your Best Choice: Active, Semi
The Flipper just emulates a NFC reader, but not a POS device which actually pulls more data. .
RFID and the Differences in Passive, Semi
Passive tags are typically made up of two parts – an integrated circuit and an antenna. No additional moving parts or batteries, just the bare necessities. Without a battery, these tags receive power as they are being read through a process called coupling. This is where they get their name – a passive tag must . See moreAt their most basic, semi-passive tags contain an integrated circuit, antenna and battery – but they aren’t limited to those three components. . See more
ppt on rfid based attendance system
The most complex of the three categories we’re covering here is the active tag. Active tags are made up of an integrated circuit, antenna, . See moreSemi-passive RFID tags look more like passive tags in terms of size and ease of manufacture. but like active tags, they incorporate a power source—usually a small, eco-friendlier battery—to . Semi-passive RFID is best suited for applications where additional features such as environmental monitoring are necessary, but the tagged items are within range of the reader or can be scanned regularly. Active. The most complex of the three categories we’re covering here is .
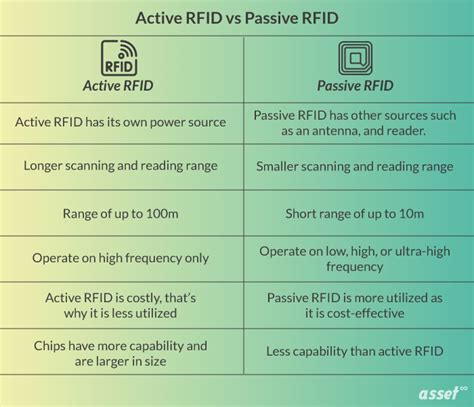
Semi-passive RFID tags look more like passive tags in terms of size and ease of manufacture. but like active tags, they incorporate a power source—usually a small, eco-friendlier battery—to improve data transmission. Active RFID systems use battery-powered RFID tags that continuously broadcast their own signal. Active RFID tags are commonly used as “beacons” to accurately track the real-time location of assets or in high-speed environments such as tolling.
Semi-passive (or battery-assisted) RFID tags contain a battery, but do not transmit a periodic signal like active RFID tags. Instead, the battery is only used to turn the tag on when a signal is received — this allows all energy from the reader’s signal to be reflected back. Semi-passive RFID tracking combines parts of the two different types of RFID tags. It has an internal battery, an RFID antenna, and data chips but no separate powered transmitter. Instead, it uses the battery to power the memory and chip so the antenna can use all the captured energy for its backscatter response. Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters.
What is active RFID? Active RFID systems use tags equipped with their power source, enabling them to broadcast signals independently. These tags have longer ranges and have their own ‘brains’ allowing them to support sensors, IOs and more compared to passive tags. Semi-passive RFID tags combine the best of both worlds: they’re powered by an external source but can also store data for later transmission without recharging by that same source. Semi-passive tags can also maintain their charge .What About Semi-Passive RFID Tags? Sitting directly between active and passive tags are semi-passive RFID tags. A semi-passive tag behaves exactly as a middle option should, by offering a mix of features taken from the capabilities of both active and .Active RFID is ideal for applications requiring dynamic, real-time tracking, such as monitoring the location and condition of high-value assets or tracking goods in transit. One of the key advantages of active RFID is its extended read range.
Semi-passive RFID is best suited for applications where additional features such as environmental monitoring are necessary, but the tagged items are within range of the reader or can be scanned regularly. Active. The most complex of the three categories we’re covering here is .Semi-passive RFID tags look more like passive tags in terms of size and ease of manufacture. but like active tags, they incorporate a power source—usually a small, eco-friendlier battery—to improve data transmission. Active RFID systems use battery-powered RFID tags that continuously broadcast their own signal. Active RFID tags are commonly used as “beacons” to accurately track the real-time location of assets or in high-speed environments such as tolling. Semi-passive (or battery-assisted) RFID tags contain a battery, but do not transmit a periodic signal like active RFID tags. Instead, the battery is only used to turn the tag on when a signal is received — this allows all energy from the reader’s signal to be reflected back.
Semi-passive RFID tracking combines parts of the two different types of RFID tags. It has an internal battery, an RFID antenna, and data chips but no separate powered transmitter. Instead, it uses the battery to power the memory and chip so the antenna can use all the captured energy for its backscatter response. Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters. What is active RFID? Active RFID systems use tags equipped with their power source, enabling them to broadcast signals independently. These tags have longer ranges and have their own ‘brains’ allowing them to support sensors, IOs and more compared to passive tags.
Semi-passive RFID tags combine the best of both worlds: they’re powered by an external source but can also store data for later transmission without recharging by that same source. Semi-passive tags can also maintain their charge .What About Semi-Passive RFID Tags? Sitting directly between active and passive tags are semi-passive RFID tags. A semi-passive tag behaves exactly as a middle option should, by offering a mix of features taken from the capabilities of both active and .
Passive RFID versus Active RFID
How to Make Your Best Choice: Active, Semi
rfid access control system china

PassNinja helps build NFC experiences across mobile Use our software and APIs to create, issue, update, and revoke passes for Apple Wallet and Google Wallet in minutes instead of months. . We built the API we wish existed, making it easy .
what is a semi active rfid|RFID and the Differences in Passive, Semi