rain rfid full form Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 . NFC playoff picture. 1. Detroit Lions 8-1 (first place, NFC North): The Lions hold this spot for home-field advantage and the lone bye by a half-game over the Eagles going into .
0 · rain rfid standard
1 · rain rfid reader
2 · rain rfid meaning
3 · rain alliance rfid
4 · rain alliance florence
5 · impinj website
6 · impinj rfid software
7 · impinj rain rfid
Here’s the full schedule. By PT Staff Updated Nov. 16, 2024. The 2025 NFL playoffs are set to begin on Saturday, January 11th, and end with the Super Bowl on Sunday, February .
rain rfid standard
rfid tags dairy cows
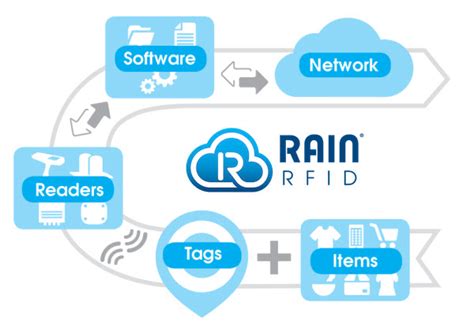
In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item with a RAIN tag.RAIN tags are items attached to the “thing” that needs to be identified. The tag is .RAIN Readers are available in many different configurations. All readers . Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 .
In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item with a RAIN tag.
Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID . Rain RFID, also known as UHF RFID, is a technology that allows for wireless identification and tracking of objects using radio frequency signals. It has gained prominence in recent years due to its versatility and functionality in a wide range of industries.RAIN RFID is the leading wireless technology providing input data into the IoT. In 2020, over 21 billion tag ICs were sold. That’s over 80 billion things identified in 2015-2020 time period. Other technologies bring other values, but none can match RAIN .The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.
How does RAIN RFID compare to other RFID technologies from a cost, quality and complexity perspective? What is the return on investment (ROI) for RFID? And these are just the most commonly asked questions.
The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed and shared via the Internet. RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and Microwave (2.45-5.8 GHz). UHF RFID is often called RAIN RFID, a name that brands passive UHF RFID products and technologies that adhere to certain industry standards and protocols. NFC, on the other hand, operates at close range, typically around 5 cm .
rain rfid reader
RAIN (derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN) is the fastest-growing segment of the RFID market. RAIN RFID is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that connects billions of.In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item with a RAIN tag.Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID . Rain RFID, also known as UHF RFID, is a technology that allows for wireless identification and tracking of objects using radio frequency signals. It has gained prominence in recent years due to its versatility and functionality in a wide range of industries.
RAIN RFID is the leading wireless technology providing input data into the IoT. In 2020, over 21 billion tag ICs were sold. That’s over 80 billion things identified in 2015-2020 time period. Other technologies bring other values, but none can match RAIN .
The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet. How does RAIN RFID compare to other RFID technologies from a cost, quality and complexity perspective? What is the return on investment (ROI) for RFID? And these are just the most commonly asked questions.
The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed and shared via the Internet. RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and Microwave (2.45-5.8 GHz). UHF RFID is often called RAIN RFID, a name that brands passive UHF RFID products and technologies that adhere to certain industry standards and protocols. NFC, on the other hand, operates at close range, typically around 5 cm .

• Al Harris' Game-Winning Pick Six in OT | Seahawks vs Packers | 2003 NFC Wild Card Game Highlights on YouTube See more
rain rfid full form|rain rfid reader