nfc card vs rfid card NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . $9.99
0 · what frequency does nfc use
1 · rfid vs nfc difference
2 · rfid tags pros and cons
3 · rfid chip pros and cons
4 · rfid and nfc difference
5 · pros and cons of nfc
6 · nfc disadvantages
7 · 13.56 mhz vs 125khz rfid
The problems seems to be that it's not possible to emulate/modify the sector 0, .The title of your post just made me realize. both the NFC Reader/Writer and the right Joy-Con have: an NFC chip; an IR blaster; So, it would theoretically be possible to write a Joy-Con firmware which transforms the Joy-Con into an NFC Reader/Writer, no? It's .
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .Do you know the difference between RFID and NFC? The differences aren’t as complicated as you might think, so we’ll highlight some, as well as practical industry uses. When it comes .
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
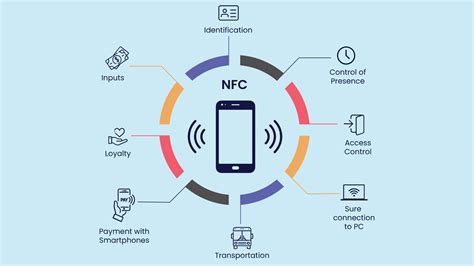
Do you know the difference between RFID and NFC? The differences aren’t as complicated as you might think, so we’ll highlight some, as well as practical industry uses. When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.
Compare NFC and RFID technologies: discover their differences, applications, and choose the right technology for your needs. Short Answer: RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
what frequency does nfc use
Explore the key differences between RFID card and NFC card in this detailed guide. Learn how each technology works, their applications, and which one is right for your needs.

While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers. NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.
NFC is commonly used for contactless payments, ticketing, and data transfer between smartphones, whereas RFID is often used for inventory management, access control, and tracking objects or assets.
NFC and RFID have different capabilities. NFC-enabled items can bring a unique web-based experience to physical products. It drives the adoption of the internet of things. On the other hand, RFID has more specific capabilities. But it does support tags. RFID cannot analyze web content such as URLs and links. Structure
rfid vs nfc difference
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
Do you know the difference between RFID and NFC? The differences aren’t as complicated as you might think, so we’ll highlight some, as well as practical industry uses. When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.
Compare NFC and RFID technologies: discover their differences, applications, and choose the right technology for your needs. Short Answer: RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
Explore the key differences between RFID card and NFC card in this detailed guide. Learn how each technology works, their applications, and which one is right for your needs. While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.NFC is commonly used for contactless payments, ticketing, and data transfer between smartphones, whereas RFID is often used for inventory management, access control, and tracking objects or assets.
rfid tags pros and cons

rfid label cost
define rfid tags
QUICK ANSWER. NFC tags and readers communicate wirelessly with each other over very short distances. Tags store a small amount of data .
nfc card vs rfid card|pros and cons of nfc