do rfid tracking work under water Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for . Card emulation mode: In this mode, data stored on cards such as smart cards are read by an NFC reader. In this mode, a device that is capable of NFC communication connects with an NFC reader in the same way as a .
0 · underwater tracking devices
1 · underwater rfid testing
2 · underwater gps technology
3 · underwater gps problems
4 · rfid underwater technology
5 · rfid underwater problems
6 · rfid in salt water
When an NFC reader is near a tag, it turns on and transmits any stored data within the microchip to the NFC-enabled device. There are five different types of NFC tags. The most basic is type 1. These can only store one kilobyte of data .
Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for .
Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for underwater applications: the High Frequency systems, operating at 13.56MHz and the Low Frequency systems, operating in the 125-134kHz band. Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for underwater applications: the High Frequency systems, operating at 13.56MHz and the Low Frequency systems, operating in the 125-134kHz band. The technology, in effect, doesn't mix well with water, which breaks down the radio waves GPS relies on to function. MIT scientists have been looking at ways to create a new type of.Ad-hoc studies have proven that in some cases RFID technology can work even under water, which is good news for underwater monitoring operations.
This paper presents the development of a device to collect and store data from a giant magnetoresistance (GMR) sensor for underwater corrosion monitoring using RFID. The findings show that RFID systems can be used to store data at near ranges of . Technologies ROI (TROI) makes tags that it claims can survive depths of 1 mile underwater (see Armored-RFID Tag Loves to Get Hammered). Omni-ID produces tags that can be read while submerged in water as well. That said, these tags must be .
underwater tracking devices
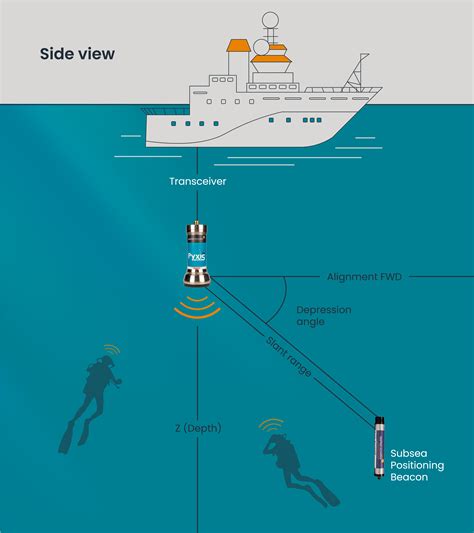
RFID transponders have been shown to be functional underwater (Benelli et al., 2009) and could provide an innovative and cheap way to track individuals during gardening efforts and after .While RFID technology is nowadays very common in many commercial and industrial sectors, from items tracking to personal identification, few studies have dealt with the chance to use RFID systems in marine or fluvial environments for underwater monitoring operations. Simply, the radio frequency on which GNSS relies (1.2Ghz to 1.6Ghz), can’t penetrate water, and actually reflects off the surface. In order to have reliable underwater tracking, acoustics is the most commonly used method.
This paper aims to discuss the theoretical transmission models for RFID systems underwater, separating them into near-field systems – which use Magnetic Induction (MI) to communicate – and far-field systems – that transfer data via Radio Frequency (RF).Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for underwater applications: the High Frequency systems, operating at 13.56MHz and the Low Frequency systems, operating in the 125-134kHz band. Due to these limitations, only two RFID technologies can be employed for underwater applications: the High Frequency systems, operating at 13.56MHz and the Low Frequency systems, operating in the 125-134kHz band. The technology, in effect, doesn't mix well with water, which breaks down the radio waves GPS relies on to function. MIT scientists have been looking at ways to create a new type of.
Ad-hoc studies have proven that in some cases RFID technology can work even under water, which is good news for underwater monitoring operations.
This paper presents the development of a device to collect and store data from a giant magnetoresistance (GMR) sensor for underwater corrosion monitoring using RFID. The findings show that RFID systems can be used to store data at near ranges of . Technologies ROI (TROI) makes tags that it claims can survive depths of 1 mile underwater (see Armored-RFID Tag Loves to Get Hammered). Omni-ID produces tags that can be read while submerged in water as well. That said, these tags must be . RFID transponders have been shown to be functional underwater (Benelli et al., 2009) and could provide an innovative and cheap way to track individuals during gardening efforts and after .While RFID technology is nowadays very common in many commercial and industrial sectors, from items tracking to personal identification, few studies have dealt with the chance to use RFID systems in marine or fluvial environments for underwater monitoring operations.
Simply, the radio frequency on which GNSS relies (1.2Ghz to 1.6Ghz), can’t penetrate water, and actually reflects off the surface. In order to have reliable underwater tracking, acoustics is the most commonly used method.

underwater rfid testing
1- Understanding NFC: A Brief Technical Overview 2- NFC on Google Pixel: A User's Guide 2.1- Setting Up NFC on Your Pixel Device 2.2- Everyday Uses for NFC on Pixel 3- Google Pixel's NFC and Mobile Payments .
do rfid tracking work under water|underwater tracking devices