rfid proximity sensor range Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a . Step 2: Your My Card contact information should be shown at the top. Select this to share your own details or locate another contact that you want to share. Step 3: Scroll down to the bottom of .
0 · rfid tags and sensors
1 · rfid sensor cost
2 · rfid proximity detector
3 · rfid card vs proximity
4 · hid vs rfid
5 · battery assisted passive rfid tags
6 · allen bradley sensaguard sensor
7 · allen bradley safety proximity sensor
The Northeastern Indiana Amateur Radio Association is a incorporated not for profit organization of amateur (ham) radio operators located in the city of Auburn in Dekalb county Indiana. First established in 1939. Our goal is to share the .
Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a different IC around which to build a reader . The read range of RFID tags can be influenced by factors such as the frequency band, the power output of the reader, the sensitivity of the tag’s antenna, and environmental .
Understanding frequency distinctions is key, as each range has unique advantages and limitations. Ultimately, choosing the right solution depends on factors like .
lg g2 nfc read write
Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a . The read range of RFID tags can be influenced by factors such as the frequency band, the power output of the reader, the sensitivity of the tag’s antenna, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for selecting the appropriate RFID technology and optimizing the read range for specific applications. Understanding frequency distinctions is key, as each range has unique advantages and limitations. Ultimately, choosing the right solution depends on factors like range, speed, and environmental conditions. By evaluating these, you can optimize processes and efficiency with RFID technology. The majority of HF RFID devices function at 13.56 MHz, with moderate radio interference sensitivity. Several uses of HF RFID involve Near Field Communication (NFC), which focuses around data transfer between two devices. This is often seen in smart payment cards and other proximity-activated devices.
By utilizing the right RFID sensor and understanding the factors that can affect its performance, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve their bottom line. RFID sensors are an increasingly popular technology used in various industries for tracking and identification.
rfid tags and sensors
Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader. Your RFID reader is connected to your antennas, you've adjusted your power settings, and you've applied your RFID tags to the items you want to track; however, you're having trouble reading your tags. In this article we will troubleshoot .
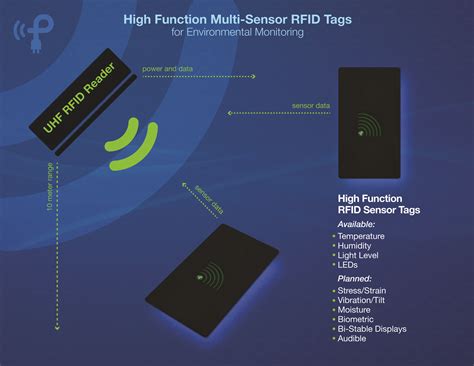
Error detection built into the RFID read operation reduces the chance of a read error. RFID also has a greater reading distance than the sensing range of a proximity sensor of comparable. RFID sensors can also be classified based on their frequency range. Low-Frequency RFID operates at frequencies below 125 kHz. High-Frequency RFID operates at frequencies above 13.56 MHz. Ultra High-Frequency RFID operates in the ultra-high frequency range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. UHF RFID tags are the most common type of tags .
Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
Here are some things I've considered: Ditch the embedded antenna on the cheap RFID reader and construct my own, larger antenna. I'd need to see if the onboard MFRC522 is up to the task of providing additional power. Look for a . The read range of RFID tags can be influenced by factors such as the frequency band, the power output of the reader, the sensitivity of the tag’s antenna, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for selecting the appropriate RFID technology and optimizing the read range for specific applications.
Understanding frequency distinctions is key, as each range has unique advantages and limitations. Ultimately, choosing the right solution depends on factors like range, speed, and environmental conditions. By evaluating these, you can optimize processes and efficiency with RFID technology.
The majority of HF RFID devices function at 13.56 MHz, with moderate radio interference sensitivity. Several uses of HF RFID involve Near Field Communication (NFC), which focuses around data transfer between two devices. This is often seen in smart payment cards and other proximity-activated devices. By utilizing the right RFID sensor and understanding the factors that can affect its performance, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve their bottom line. RFID sensors are an increasingly popular technology used in various industries for tracking and identification. Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader.
Your RFID reader is connected to your antennas, you've adjusted your power settings, and you've applied your RFID tags to the items you want to track; however, you're having trouble reading your tags. In this article we will troubleshoot . Error detection built into the RFID read operation reduces the chance of a read error. RFID also has a greater reading distance than the sensing range of a proximity sensor of comparable.
ios nfc reader tutorial
RFID sensors can also be classified based on their frequency range. Low-Frequency RFID operates at frequencies below 125 kHz. High-Frequency RFID operates at frequencies above 13.56 MHz. Ultra High-Frequency RFID operates in the ultra-high frequency range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. UHF RFID tags are the most common type of tags .

rfid sensor cost
rfid proximity detector

iphone 11 no nfc tag reader
rfid card vs proximity
$8.99
rfid proximity sensor range|hid vs rfid