tracking kids rfid subdermal Despite a lack of evidence demonstrating invasive use or even technical capability of microchip implants, they have been the subject of many conspiracy theories.The Southern Poverty Law Center reported in 2010 that on the Christian right, there were concerns that . See more
The Drive with Bill Cameron, ESPN 106.7’s weekday afternoon sports show, is a fast-paced, in-depth look at the world of sports with a focus on Auburn University and local high schools. Live from 4:00 p.m.-6:00 p.m., the show has been .
0 · rfid microchips
1 · rfid chip implantation
2 · rfid chip for subway
NFC Tools - Effortless NFC Tag Management Unlock the power of NFC technology with NFC Tools, your all-in-one solution for reading, writing, and managing NFC tags. . NFC reader, writer & scanner FREE AI UTILS COMPANY LIMITED Designed for iPad Free; Screenshots. iPad iPhone . Mac Requires macOS 11.0 or later and a Mac with Apple M1 chip or .
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. This type of subdermal implant usually contains a . See more
• 1998: The first experiments with a radio-frequency identification (RFID) implant were carried out in 1998 by the British scientist Kevin Warwick. . See more• Brain implant• Skin• Dental implant See moreFor Microchip implants that are encapsulated in silicate glass, there exists multiple methods to embed the device subcutaneously ranging from placing the microchip implant in a syringe or trocar and piercing under the flesh (subdermal) then releasing the . See moreInfectionInfection has been cited as a source of failure within RFID and related microchip implanted individuals, either due to improper implantation techniques, implant rejections or corrosion of implant elements. See more
Despite a lack of evidence demonstrating invasive use or even technical capability of microchip implants, they have been the subject of many conspiracy theories.The Southern Poverty Law Center reported in 2010 that on the Christian right, there were concerns that . See moreA few jurisdictions have researched or preemptively passed laws regarding human implantation of microchips.United StatesIn the United States, many states such as Wisconsin (as . See more

rfid microchips
The general public are most familiar with microchips in the context of identifying pets.In popular cultureImplanted individuals are considered to be grouped together as part of the transhumanism See more But implanted, contactless RFID microchips could also be inserted in places of .A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Tracking Chip Implant For Babies. What Is A Human Microchip. A human microchip, to put it simply, is a minuscule device embedded under your skin. Leveraging RFID technology, this microchip works as a personal identifier. But implanted, contactless RFID microchips could also be inserted in places of the body other than the brain, for more everyday but equally essential purposes—such as allowing those with disabilities to automatically open doors. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . You might find yourself researching microchip tracking devices for humans, implantable under a child’s skin, but do they actually exist? In this article, our experts at Tracking System Direct will tackle this topic head-on, providing .
Key Takeaways. Theoretically, RFID implants offer practical benefits as contactless payments, unlocking doors, and accessing medical data, with just a wave of your hand. However, the implants still face challenges such as safety concerns, potential .
A user with a microchip implanted in them could potentially be tracked wherever they go. Information from RFID chips is easily obtained, meaning the everyday movements of a citizen could be monitored and exploited for nefarious purposes. Medical complications. The potential biological complications are also somewhat unknown. It's a useful technology application: insert a subdermal radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip somewhere the animal can't get to it – such as the nape of its neck – and a whole world of digital data opens up. People are spending thousands of dollars to have GPS tracking-enabled RFID chips implanted under their skin and the skin of family members. According to Xega, the Mexican company that sells the RFID chips and performs the implants, the chip is implanted in the tissue between the shoulder and elbow. Specific security vulnerabilities were identified in humans implanted with radio frequency identification (RFID) technology, which “uses communication via electromagnetic waves to exchange data between an interrogator (reader) and an object called the transponder for identification and tracking purposes” [117].
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Tracking Chip Implant For Babies. What Is A Human Microchip. A human microchip, to put it simply, is a minuscule device embedded under your skin. Leveraging RFID technology, this microchip works as a personal identifier.
But implanted, contactless RFID microchips could also be inserted in places of the body other than the brain, for more everyday but equally essential purposes—such as allowing those with disabilities to automatically open doors. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . You might find yourself researching microchip tracking devices for humans, implantable under a child’s skin, but do they actually exist? In this article, our experts at Tracking System Direct will tackle this topic head-on, providing .Key Takeaways. Theoretically, RFID implants offer practical benefits as contactless payments, unlocking doors, and accessing medical data, with just a wave of your hand. However, the implants still face challenges such as safety concerns, potential .
A user with a microchip implanted in them could potentially be tracked wherever they go. Information from RFID chips is easily obtained, meaning the everyday movements of a citizen could be monitored and exploited for nefarious purposes. Medical complications. The potential biological complications are also somewhat unknown.
It's a useful technology application: insert a subdermal radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip somewhere the animal can't get to it – such as the nape of its neck – and a whole world of digital data opens up. People are spending thousands of dollars to have GPS tracking-enabled RFID chips implanted under their skin and the skin of family members. According to Xega, the Mexican company that sells the RFID chips and performs the implants, the chip is implanted in the tissue between the shoulder and elbow.
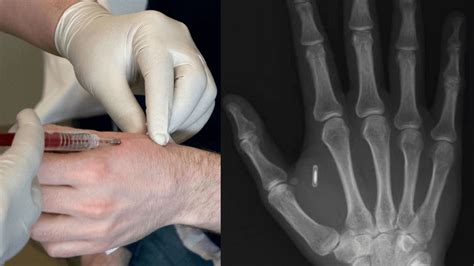
rfid chip implantation
Languages. Kotlin 100.0%. Android NFC read and write example. Contribute to codexpedia/android_nfc_read_write development by creating an account on GitHub.
tracking kids rfid subdermal|rfid chip implantation