emv vs rfid debit card EMV is the payment technology used by all credit cards and debit cards that have an embedded chip, which lets the cardholder more securely make a transaction. "EMV" stands for Europay, Mastercard and Visa, the companies that developed EMV payment technology in 1994. Check out our nfc cards amibo selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade .
0 · what is emv credit card
1 · how to use emv card
2 · how does emv card work
3 · foreign emv credit card
4 · emv vs rfid card
5 · emv credit card types
6 · emv chip vs rfid
7 · emv chip and pin card
Cek saldo melalui layanan ini bisa dilakukan dengan cara berikut. Kunjungi halaman ib mandiri. Ketikkan User ID dan PIN Internet Banking pada kolom yang tersedia. Pilih menu “Uang .
Contactless covers everything from NFC to QR codes. We look at the various technologies that underpin your contactless transactions and the difference between them all. Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a contactless and wireless way to transfer data through radio waves. EMV is the payment technology used by all credit cards and debit cards that .
Contactless covers everything from NFC to QR codes. We look at the various technologies that underpin your contactless transactions and the difference between them all. Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a contactless and wireless way to transfer data through radio waves. EMV is widely considered to be the most secure way to process credit and debit card payments. This is because EMV chip cards are very difficult to counterfeit. Additionally, EMV cards create a unique transaction code that cannot be reused. EMV is the payment technology used by all credit cards and debit cards that have an embedded chip, which lets the cardholder more securely make a transaction. "EMV" stands for Europay, Mastercard and Visa, the companies that developed EMV payment technology in 1994.
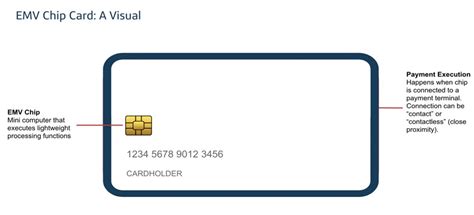
While RFID technology can be used for contactless payment processing, it is not the same as EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) technology. EMV technology refers specifically to chip-based credit and debit cards that process payments using . An EMV chip, that little rectangle or square, is a computer chip embedded in credit cards and debit cards. The chip sends a secure, one-time code when you put it in a card reader that the retailer uses to process the transaction.
While traditional cards are swiped and EMV cards are inserted, contactless cards must be tapped or placed within roughly one inch of the point of sale terminal. With contactless payments, your transaction will be securely processed within a matter of seconds.
Contactless payments have become the norm, but terms like NFC, EMV, and RFID can be confusing. This article highlights the history and underlying technologies of contactless payments, from RFID, which emerged in the 1980s for inventory tracking, to . Standard EMV payments use the chip embedded on a credit or debit card to gather the card details and process payments. When it comes to NFC payments, the card or digital wallet is placed near the payment terminal and RFID is used to . EMV, or Europay-Mastercard-Visa, is a global standard for credit and debit card transactions. It uses chip technology to increase security and reduce fraud in card-present transactions. RFID, or radio frequency identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data and uniquely identify an object.
EMV is generally considered more secure than RFID because it uses a chip-and-PIN system that encrypts data during transactions and creates unique identifiers for each cardholder within the system.
Contactless covers everything from NFC to QR codes. We look at the various technologies that underpin your contactless transactions and the difference between them all. Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a contactless and wireless way to transfer data through radio waves. EMV is widely considered to be the most secure way to process credit and debit card payments. This is because EMV chip cards are very difficult to counterfeit. Additionally, EMV cards create a unique transaction code that cannot be reused. EMV is the payment technology used by all credit cards and debit cards that have an embedded chip, which lets the cardholder more securely make a transaction. "EMV" stands for Europay, Mastercard and Visa, the companies that developed EMV payment technology in 1994. While RFID technology can be used for contactless payment processing, it is not the same as EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) technology. EMV technology refers specifically to chip-based credit and debit cards that process payments using .
An EMV chip, that little rectangle or square, is a computer chip embedded in credit cards and debit cards. The chip sends a secure, one-time code when you put it in a card reader that the retailer uses to process the transaction.
While traditional cards are swiped and EMV cards are inserted, contactless cards must be tapped or placed within roughly one inch of the point of sale terminal. With contactless payments, your transaction will be securely processed within a matter of seconds. Contactless payments have become the norm, but terms like NFC, EMV, and RFID can be confusing. This article highlights the history and underlying technologies of contactless payments, from RFID, which emerged in the 1980s for inventory tracking, to . Standard EMV payments use the chip embedded on a credit or debit card to gather the card details and process payments. When it comes to NFC payments, the card or digital wallet is placed near the payment terminal and RFID is used to .
EMV, or Europay-Mastercard-Visa, is a global standard for credit and debit card transactions. It uses chip technology to increase security and reduce fraud in card-present transactions. RFID, or radio frequency identification, is a technology that uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data and uniquely identify an object.

what is emv credit card
rfid based door lock system report
rfid based car parking system working
For the Note 9, you cannot replace the battery. ZeroLemon's and other manufacturer's solution to that, is a "battery case", providing an additional 10,000 mAh on top of the existing 4,000 mAh. .
emv vs rfid debit card|emv vs rfid card