early rfid supply chain chip Two professors there, David Brock and Sanjay Sarma, had been doing some research into the possibility of putting low-cost RFID tags on all products made to track them through the supply chain. Their idea was to put only a serial number on the tag to keep the . Step 4: Choose the Copy Option. Select the “Copy” or “Clone” option within the app’s interface. This will initiate the process of copying an NFC tag. Step 5: Place the Original Tag Near Your Device. Take the original NFC .
0 · who invented rfid technology
1 · what is rfid
2 · rfid technology
3 · rfid supply chain framework
4 · rfid supply chain
5 · history of rfid systems
6 · history of rfid identification
7 · first rfid technology
The Cleveland Browns and Houston Texans continued to defy expectations with Week 11 wins that kept them ahead of the competition in the AFC wild-card race..Find out which teams are winning the 2024 playoff race. Check out the NFL Playoff Picture for the latest team performance stats and playoff eliminations. Learn more.
who invented rfid technology
Two professors there, David Brock and Sanjay Sarma, had been doing some research into the possibility of putting low-cost RFID tags on all products made to track them through the supply chain. Their idea was to put only a serial number on the tag to keep the . Reyes et al. (2021) examined the use of RFID as an automatic identification data capture (AIDC) technology and as a tool for data analysis. The primary purpose of this paper . Two professors there, David Brock and Sanjay Sarma, had been doing some research into the possibility of putting low-cost RFID tags on all products made to track them through the supply chain. Their idea was to put only a serial number on the tag to keep the price down (a simple microchip that stored very little information would be less . Behind the scenes, the use of RFID is crucial in modern warehouses and throughout the supply chain. Featuring a system of tags with encoded data, this groundbreaking technology makes today’s supply chain safer, more efficient, and more cost-effective.
Reyes et al. (2021) examined the use of RFID as an automatic identification data capture (AIDC) technology and as a tool for data analysis. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide an example of how RFID, for collecting timely and relevant data, could be applied to supply chain analytics.RFID and the convergence of those Industry 4.0 technologies will soon change the landscape of supply chain management. Early RFID Academic interest in RFID generated a fast-growing body of literature. General research topics include RFID technology and appli-cations, benets, and business value.
schreiner medipharm smart blister card
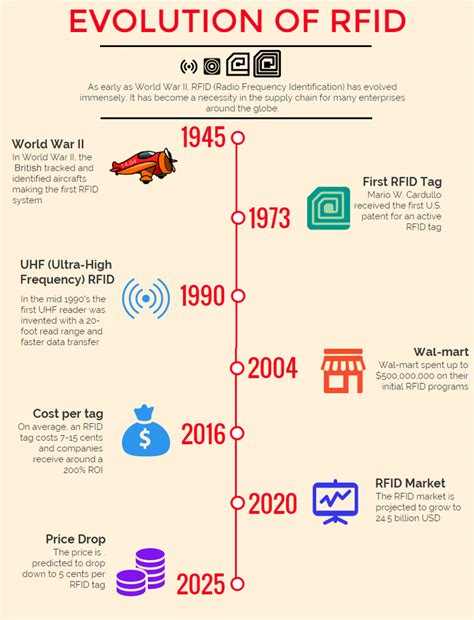
In the early 2000s, RFID tags cost 50 to 75 cents each — now, they’re around 3 to 8 cents each. Distributing the benefits RFID may save retailers time, but it doesn’t save manufacturers time. RFID timeline: 1973 - RFID first patented The first patent for commercial RFID tags was granted in 1973 to Mario W. Cardullo, whose RFID tag had a rewritable memory. The same year, California entrepreneur Charles Walton received a patent for a passive transponder used to unlock a door without a key. RFID – Radio-Frequency Identification – uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects which carry either a passive or active tag. Unlike passive tags that require energy from nearby RFID readers to be detected, active tags have their own power source to broadcast their unique identification number and thanks to this, the tags . This paper provides a state of the art on RFID technology in Supply chain management. It presents technical characteristics of existing RFID systems, a guideline for RFID deployment, and some applications in Supply chains.
This paper offers a major contribution to understanding the current status of the adoption of RFID in European supply chains. This understanding is put in the context of the wider literatures on supply chain management and the adoption of information systems and technology. RFID provides real-time data on supply chain operations, such as the location of goods, the status of shipments, and the performance of supply chain partners. This information lets companies quickly respond to disruptions and make informed decisions to improve supply chain efficiency.
Two professors there, David Brock and Sanjay Sarma, had been doing some research into the possibility of putting low-cost RFID tags on all products made to track them through the supply chain. Their idea was to put only a serial number on the tag to keep the price down (a simple microchip that stored very little information would be less . Behind the scenes, the use of RFID is crucial in modern warehouses and throughout the supply chain. Featuring a system of tags with encoded data, this groundbreaking technology makes today’s supply chain safer, more efficient, and more cost-effective. Reyes et al. (2021) examined the use of RFID as an automatic identification data capture (AIDC) technology and as a tool for data analysis. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide an example of how RFID, for collecting timely and relevant data, could be applied to supply chain analytics.RFID and the convergence of those Industry 4.0 technologies will soon change the landscape of supply chain management. Early RFID Academic interest in RFID generated a fast-growing body of literature. General research topics include RFID technology and appli-cations, benets, and business value.
In the early 2000s, RFID tags cost 50 to 75 cents each — now, they’re around 3 to 8 cents each. Distributing the benefits RFID may save retailers time, but it doesn’t save manufacturers time.
RFID timeline: 1973 - RFID first patented The first patent for commercial RFID tags was granted in 1973 to Mario W. Cardullo, whose RFID tag had a rewritable memory. The same year, California entrepreneur Charles Walton received a patent for a passive transponder used to unlock a door without a key.
RFID – Radio-Frequency Identification – uses electromagnetic fields to identify and track objects which carry either a passive or active tag. Unlike passive tags that require energy from nearby RFID readers to be detected, active tags have their own power source to broadcast their unique identification number and thanks to this, the tags . This paper provides a state of the art on RFID technology in Supply chain management. It presents technical characteristics of existing RFID systems, a guideline for RFID deployment, and some applications in Supply chains.This paper offers a major contribution to understanding the current status of the adoption of RFID in European supply chains. This understanding is put in the context of the wider literatures on supply chain management and the adoption of information systems and technology.
what is rfid
rfid technology
rfid supply chain framework
Amazon.com : Hicarer NFC 215 Cards, NTAG215 NFC Round Cards NFC 215 Card Tag Compatible with TagMo NFC Enabled Mobile Phones and Devices .
early rfid supply chain chip|rfid supply chain framework