rfid read count To summarize, RFID tags can be read one after another very quickly, but for a very dense tag population, the tags would need to be in the read field for a few seconds. For more information on how to set up a UHF system to read dense tag populations, see the answer to . All playoff games aired on network television. This was the NFL's standard policy through the end of the previous television contract in 2013. After airing one game exclusively on . See more
0 · rfid tag reading range
1 · rfid tag read range chart
2 · rfid reading time
3 · rfid reading range
4 · rfid maximum read range
5 · rfid longer read range
6 · how many rfid tags can i read
7 · how fast is rfid reading
Tap-to-pay cards. Many credit and debit cards are NFC-enabled, so they can be used to make purchases with tap to pay. A shopper would just have to tap or hover their card over the . See more
To summarize, RFID tags can be read one after another very quickly, but for a very dense tag population, the tags would need to be in the read field for a few seconds. For more information on how to set up a UHF system to read dense tag populations, see the answer to .
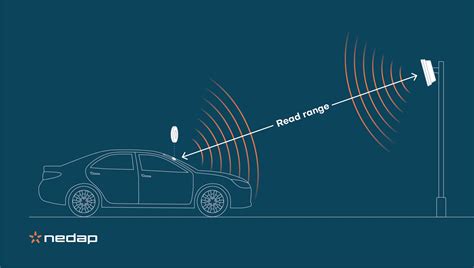
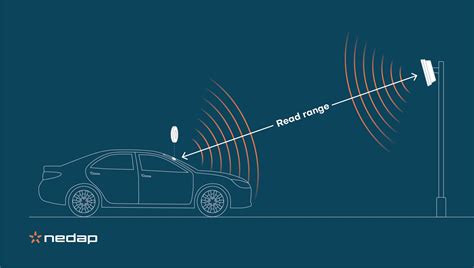
RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data . Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data. To summarize, RFID tags can be read one after another very quickly, but for a very dense tag population, the tags would need to be in the read field for a few seconds. For more information on how to set up a UHF system to read dense tag populations, see the answer to a recent Ask the Experts question, How Can I Read 1,000 Tagged Apparel Items . #1. What Is Read Range? Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader. #2. How Is Read Range Determined? Generally, the manufacturer spec sheet includes RFID read range information.
RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags. Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
I have seen more than 50 passive high-frequency (HF) and ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) tags read within a second. So the read time is mere milliseconds. But the big advantage RFID offers over bar codes is that RFID does not require line of sight. Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. Antenna Cable Selection – Power Loss. Environment Factors – Metal, Water. 1.
Generally speaking, the reading speed of ultra-high frequency RFID is at a rate that can read hundreds of tags per second. More importantly, the technical characteristics of UHF RFID batch reading have greatly improved the company’s inventory management efficiency and .
Read-Only vs. Read-Write: Read-only RFID tags usually have fixed, pre-programmed data that cannot be modified or updated. This limited data storage capacity is sufficient for applications that only require basic identification or tracking information. Easily reading data from RFID tags allows you to identify single items or entire batches of goods simultaneously. To help you understand every element involved, here’s what you need to know about storing and reading data on and from RFID tags.Read range for an RFID tag is affected by many factors, including: - Passive, BAP, NFC or Active. - RFID frequency - LF, HF or UHF. - Surrounding materials. - Type of tag. - Type of reader. - Orientation. - Time to read. - Number of tags being read. - Density of tags.
To summarize, RFID tags can be read one after another very quickly, but for a very dense tag population, the tags would need to be in the read field for a few seconds. For more information on how to set up a UHF system to read dense tag populations, see the answer to a recent Ask the Experts question, How Can I Read 1,000 Tagged Apparel Items . #1. What Is Read Range? Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader. #2. How Is Read Range Determined? Generally, the manufacturer spec sheet includes RFID read range information.RFID uses radio waves produced by a reader to detect the presence of (then read the data stored on) an RFID tag. Tags are embedded in small items like cards, buttons, or tiny capsules. These readers also use radio waves in some systems to write new information to the tags. Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
I have seen more than 50 passive high-frequency (HF) and ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) tags read within a second. So the read time is mere milliseconds. But the big advantage RFID offers over bar codes is that RFID does not require line of sight. Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. Antenna Cable Selection – Power Loss. Environment Factors – Metal, Water. 1.Generally speaking, the reading speed of ultra-high frequency RFID is at a rate that can read hundreds of tags per second. More importantly, the technical characteristics of UHF RFID batch reading have greatly improved the company’s inventory management efficiency and . Read-Only vs. Read-Write: Read-only RFID tags usually have fixed, pre-programmed data that cannot be modified or updated. This limited data storage capacity is sufficient for applications that only require basic identification or tracking information.
Easily reading data from RFID tags allows you to identify single items or entire batches of goods simultaneously. To help you understand every element involved, here’s what you need to know about storing and reading data on and from RFID tags.

rfid tag reading range

java smart card reader example
Security risks: NFC tags themselves are typically very secure. They can only hold a small .
rfid read count|rfid longer read range