radio frequency identification rfid tag mbus 303 A Radio-Oriented Introduction to RFID—Protocols, Tags and Applications. By Daniel M. Dobkin, Enigmatics, and Titus Wandinger, WJ Communications. The authors’ instructional presentation of RFID tech-nology and applications continues with this . NFC/RFID (Replaced by new RFID) Be sure to check out the newer model - Elo .
0 · what is rfid
1 · rfid bar code
2 · mis 303 quizlet
3 · mis 303 final rfid tag
Hello Everyone!!!! I have a question about Samsung Pay on the Gear S3 .
956 solutions. Terms in this set (9) RFID - Radio Frequency Identification. Uses electronic tags and labels to identify objects wirelessly over short distances. RFID Tag. An electronic .The Mantis-series 303 MHz asset tag is an active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) beacon device used to locate, track, and identify assets. Paired with RF Code's Mantis II readers, .
956 solutions. Terms in this set (9) RFID - Radio Frequency Identification. Uses electronic tags and labels to identify objects wirelessly over short distances. RFID Tag. An electronic identification device made up of a chip and antenna. RFID reader (interrogator) a transmitter/receiver that reads the contents of the RFID tags in the area.The Mantis-series 303 MHz asset tag is an active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) beacon device used to locate, track, and identify assets. Paired with RF Code's Mantis II readers, these tags become integral components in highly scalable asset tracking environments.A Radio-Oriented Introduction to RFID—Protocols, Tags and Applications. By Daniel M. Dobkin, Enigmatics, and Titus Wandinger, WJ Communications. The authors’ instructional presentation of RFID tech-nology and applications continues with this .• Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a
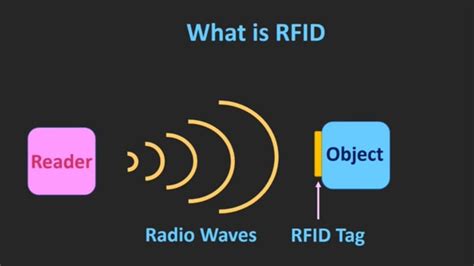
RFID stands for radio frequency identification. It is an automatic identification technology whereby digital data is encoded in an RFID tag or "smart label" and is captured by a reader using radio waves. A pulsed beam of radio waves from the transmitter strikes the tag, making it give off a precise frequency radio signal. The receiver picks up the signal, verifies that it's at the correct frequency, and then sets off the alarm. RFID is a powerful tool for automatic identification, tracking, and data capture in a wide range of industries and applications. Here, we will delve deeper into how RFID technology leverages radio waves or electromagnetic signals to facilitate wireless communication between RFID tags and readers.
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.In short, RFID tags are small contactless chip devices that communicate data through radio waves. They combine radio frequency identification technology and microelectronics technology to achieve barrier-free, long-distance automatic identification and data exchange of . An RFID tag is a tiny computer chip attached to an antenna in a compact form, transmitting information to an RFID reader through radio waves. There are several types of RFID tags, each operating at a different frequency. These tags can withstand abrasive conditions, making them a durable barcode label alternative.
what is rfid
956 solutions. Terms in this set (9) RFID - Radio Frequency Identification. Uses electronic tags and labels to identify objects wirelessly over short distances. RFID Tag. An electronic identification device made up of a chip and antenna. RFID reader (interrogator) a transmitter/receiver that reads the contents of the RFID tags in the area.The Mantis-series 303 MHz asset tag is an active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) beacon device used to locate, track, and identify assets. Paired with RF Code's Mantis II readers, these tags become integral components in highly scalable asset tracking environments.
A Radio-Oriented Introduction to RFID—Protocols, Tags and Applications. By Daniel M. Dobkin, Enigmatics, and Titus Wandinger, WJ Communications. The authors’ instructional presentation of RFID tech-nology and applications continues with this .
• Tag or transponder: a RFID tag is a tiny radio device that is also referred to as a transponder, smart tag, smart label or radio bar code. The tag comprises a simple silicon microchip (typically less than half a
RFID stands for radio frequency identification. It is an automatic identification technology whereby digital data is encoded in an RFID tag or "smart label" and is captured by a reader using radio waves.
A pulsed beam of radio waves from the transmitter strikes the tag, making it give off a precise frequency radio signal. The receiver picks up the signal, verifies that it's at the correct frequency, and then sets off the alarm. RFID is a powerful tool for automatic identification, tracking, and data capture in a wide range of industries and applications. Here, we will delve deeper into how RFID technology leverages radio waves or electromagnetic signals to facilitate wireless communication between RFID tags and readers.RFID (radio frequency identification) is a form of wireless communication that incorporates the use of electromagnetic or electrostatic coupling in the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum to uniquely identify an object, animal or person.
In short, RFID tags are small contactless chip devices that communicate data through radio waves. They combine radio frequency identification technology and microelectronics technology to achieve barrier-free, long-distance automatic identification and data exchange of .
rfid bar code
list of different smart card chips
linux smart card reader writer
limitations of smart card
mis 303 quizlet
When Apple released its new iPhone 5 in September 2012, many in the Near .
radio frequency identification rfid tag mbus 303|rfid bar code