active rfid sensor technology Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna. The easiest way to write data to an NFC tag or card is by using your smartphone. .
0 · rfid sensor simulation
1 · rfid sensor price
2 · rfid sensor meaning
3 · rfid sensor full form
4 · rfid sensor datasheet
5 · rfid sensor cost
6 · rfid is involved when using
7 · rfid full form in computer
NFC is an ISO standard, so if you credit card is NFC compatible, your phone should be able to .1. Turn on near field communication (NFC) Next: 2. Set Google Pay as your default payment app. To use Google Wallet, make sure NFC is enabled and set up correctly on your device. On your Android device, open the Settings app. In the search bar, type “NFC.”. Make sure that the NFC .
Active RFID systems use battery-powered RFID tags that continuously broadcast their own signal. Active RFID tags are commonly used as “beacons” to accurately track the real-time location of assets or in high-speed environments such as tolling. Active RFID systems (otherwise known as active RTLS) use battery-powered sensor tags that connect to various access points throughout an area (like a building) and transfer data to the cloud. Active RFID is commonly used for real-time location tracking.Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna.The process of identifying an asset using RFID involves three main components – the tag itself, a reader or scanner device, and a database or software system for storing and managing data. The first step is encoding information on to each unique tag before attaching it to an asset.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is revolutionizing how we track, manage, and interact with objects around us. But within this exciting realm lies a crucial choice: active vs. passive RFID. Each technology boasts unique advantages, .
There are two main types of RFID tags: Active RFID. An active RFID tag has its own power source, often a battery. Passive RFID. A passive RFID tag receives its power from the reading antenna, whose electromagnetic wave induces a current in the RFID tag's antenna.
Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters.
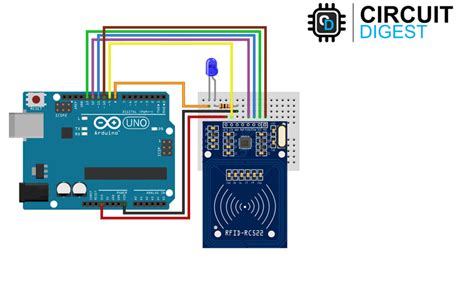
A sensor is an energy-saving active RFID tag that goes into sleep mode to save power when it is not within the reader’s range. Once the reader signal is detected, it is activated and sends a signal containing relevant data. What is active RFID? Active RFID systems use tags equipped with their power source, enabling them to broadcast signals independently. These tags have longer ranges and have their own ‘brains’ allowing them to support sensors, IOs and more compared to passive tags.
When it comes to tracking and monitoring assets anytime, from anywhere, the rush is on to implement an indoor positioning solution that incorporates active radio frequency identification (RFID) into real-time location system (RTLS) technology. Why? Active RFID systems use battery-powered RFID tags that continuously broadcast their own signal. Active RFID tags are commonly used as “beacons” to accurately track the real-time location of assets or in high-speed environments such as tolling.
Active RFID systems (otherwise known as active RTLS) use battery-powered sensor tags that connect to various access points throughout an area (like a building) and transfer data to the cloud. Active RFID is commonly used for real-time location tracking.
Active RFID (radio frequency identification) tags are continuously operating, battery-powered sensors that gather and transmit data to a reading device. An active RFID system consists of a reader, tag and antenna.The process of identifying an asset using RFID involves three main components – the tag itself, a reader or scanner device, and a database or software system for storing and managing data. The first step is encoding information on to each unique tag before attaching it to an asset.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is revolutionizing how we track, manage, and interact with objects around us. But within this exciting realm lies a crucial choice: active vs. passive RFID. Each technology boasts unique advantages, .
There are two main types of RFID tags: Active RFID. An active RFID tag has its own power source, often a battery. Passive RFID. A passive RFID tag receives its power from the reading antenna, whose electromagnetic wave induces a current in the RFID tag's antenna. Active RFID tags, distinguished by their internal power source, operate using a battery to actively transmit signals to RFID readers. The inclusion of a power source empowers active tags to broadcast signals over longer distances, enabling read ranges that can extend up to hundreds of meters.A sensor is an energy-saving active RFID tag that goes into sleep mode to save power when it is not within the reader’s range. Once the reader signal is detected, it is activated and sends a signal containing relevant data.
What is active RFID? Active RFID systems use tags equipped with their power source, enabling them to broadcast signals independently. These tags have longer ranges and have their own ‘brains’ allowing them to support sensors, IOs and more compared to passive tags.
cingular 64k smart chip sim card
Beep Cards can be used to pay for fares of LRT1, LRT2, and MRT3, and select bus lines such as the BGC Bus, TAS Trans / San Agustin, Precious Grace Transport, LNC Link, and P2P Bus (Ube Express, RRCG Transport). Payments also expanded to include . See more
active rfid sensor technology|rfid sensor cost