nfc tag vs rfid NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . Here’s how it works. (Image credit: Shutterstock) Keeping your credit card details safe from hackers just got a whole lot more difficult following a new data breach at a payment gateway provider .
0 · wifi tags vs rfid
1 · rfid technology disadvantages
2 · rfid chip pros and cons
3 · read rfid tags with nfc
4 · pros and cons of nfc
5 · nfc and rfid difference
6 · can nfc reader read rfid
7 · 13.56 mhz vs 125khz rfid
NFL Playoff Schedule 2017: Dates, Kickoff Times, TV Listings, Results For Each Game . WILD-CARD ROUND Saturday, Jan. 7 AFC: Houston Texans 27, Oakland Raiders 14 . NFC .
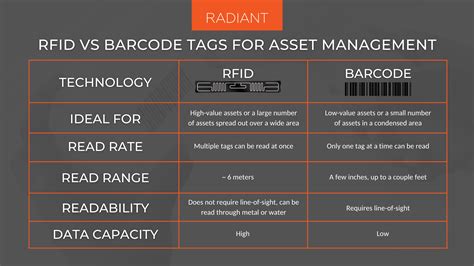
RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies . NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and .
RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes. NFC is designed to be a secure form of data exchange, and an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. This unique feature allows NFC devices to communicate peer-to-peer. Long Answer: By definition, RFID is the method of uniquely identifying items using radio waves.
RFID tags are often used within a few meters, while NFC tags are limited to centimeters. Understanding the overlap and differences between RFID and NFC will help you decide which is right for you. Each serves users with unique functionality that can help to streamline business operations and better serve your customers.
RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance.
RFID and NFC systems use short-range communication to read the ID information on tags. They find use in many spheres of life: contactless payment transactions, asset tracking, real time location systems, access control, retail, marketing, and more. NFC devices operate at the same frequency as high frequency RFID readers and tags — 13.56 MHz. But unlike RFID devices and tags, NFC does not have a range from 25 meters to 100 meters. Instead, NFC takes advantage of the short read range limitations of . While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
One of the key differences between RFID and NFC is the range of their respective communication protocols. RFID technology has a much longer read range compared to NFC. Passive RFID tags can typically be read from a distance of several meters, while active RFID tags can be detected from even further away, up to hundreds of meters in some cases. RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes. NFC is designed to be a secure form of data exchange, and an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. This unique feature allows NFC devices to communicate peer-to-peer. Long Answer: By definition, RFID is the method of uniquely identifying items using radio waves.
RFID tags are often used within a few meters, while NFC tags are limited to centimeters. Understanding the overlap and differences between RFID and NFC will help you decide which is right for you. Each serves users with unique functionality that can help to streamline business operations and better serve your customers.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not suitable for large-scale tracking applications due to its short communication distance.
RFID and NFC systems use short-range communication to read the ID information on tags. They find use in many spheres of life: contactless payment transactions, asset tracking, real time location systems, access control, retail, marketing, and more. NFC devices operate at the same frequency as high frequency RFID readers and tags — 13.56 MHz. But unlike RFID devices and tags, NFC does not have a range from 25 meters to 100 meters. Instead, NFC takes advantage of the short read range limitations of .
wifi tags vs rfid
While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
smart trip card 7 days
smart talk same sim card same phone number

AFC Miami Dolphins (9-3) Baltimore Ravens (9-3) Kansas City Chiefs (8-4) See more
nfc tag vs rfid|nfc and rfid difference