rfid antenna read range Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. . My chip is broken in the gamepad, was gonna crack it open, buy a 3DS adapter, bust that open, and plug in the working antenna. Hardware/plug wise, should it work? HeroC114 posted.
0 · rfid tag reading range
1 · rfid tag read range chart
2 · rfid reading range
3 · rfid longer read range
4 · rfid antenna reading range
5 · rfid antenna read zone
6 · rfid antenna guide
7 · best rfid antenna for reading
$19.45
Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. .Several factors determine the read range generated by an RFID antenna such as .
Unlike read range, a read zone is describing a range of coverage that .Several factors determine the read range generated by an RFID antenna such as reader transmit power, amount of cable loss, coupling technique, antenna gain, and antenna beamwidth. A . Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. Antenna Cable Selection – Power Loss. Environment Factors – Metal, Water. 1.Several factors determine the read range generated by an RFID antenna such as reader transmit power, amount of cable loss, coupling technique, antenna gain, and antenna beamwidth. A key aspect of any RFID antenna is whether it is a far-field or near-field antenna.
Unlike read range, a read zone is describing a range of coverage that extends around the RFID antenna with varying boundaries. The read range can generally be used to determine the hypothetical distance at which a tag can . HID presents eight FAQ's regarding RFID Tag Read Range and which to consider when selecting a new tag for business process and performance. Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
We’ll look at how we can make use of COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software to determine the operating read range of a passive RFID tag powered by a reader’s interrogating field. Additionally, we will look at how we can maximize this operating range by optimizing the tag’s antenna design.The RFID reader antenna constructs data information interaction with the label by transmitting and receiving radio waves. The design and selection of antennas have a direct impact on the signal transmission range, directionality and overall efficiency of the RFID system.Directional antennas can focus RFID signals in specific directions, making them suitable for applications that require precise read and write range. It can provide high-quality signal transmission in specific areas and is widely used in access . Designing an RFID antenna requires a methodical approach, starting with the selection of the operational frequency and appropriate antenna type, followed by detailed simulation and modeling to optimize its design.
Testing the read range of a UHF RFID antenna is a critical step in ensuring the optimal performance of your RFID system. By following these nine steps, you can accurately determine the effective read range and make any necessary adjustments to optimize the system. Here are the 6 factors that most commonly affect RFID read range. Contents. RFID Antenna Selection – Gain, Beamwidth. RFID Tag Selection and Positioning – Size, Orientation, Angle, Placement. RFID Reader Settings – Transmit Power, Receive Sensitivity. Antenna Cable Selection – Power Loss. Environment Factors – Metal, Water. 1.
Several factors determine the read range generated by an RFID antenna such as reader transmit power, amount of cable loss, coupling technique, antenna gain, and antenna beamwidth. A key aspect of any RFID antenna is whether it is a far-field or near-field antenna. Unlike read range, a read zone is describing a range of coverage that extends around the RFID antenna with varying boundaries. The read range can generally be used to determine the hypothetical distance at which a tag can . HID presents eight FAQ's regarding RFID Tag Read Range and which to consider when selecting a new tag for business process and performance. Read range refers to the maximum distance within which an RFID tag can detect radio waves from an RFID reader. Whenever the tag is within this range, it becomes active and allows the reader to capture the data.
We’ll look at how we can make use of COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation software to determine the operating read range of a passive RFID tag powered by a reader’s interrogating field. Additionally, we will look at how we can maximize this operating range by optimizing the tag’s antenna design.The RFID reader antenna constructs data information interaction with the label by transmitting and receiving radio waves. The design and selection of antennas have a direct impact on the signal transmission range, directionality and overall efficiency of the RFID system.Directional antennas can focus RFID signals in specific directions, making them suitable for applications that require precise read and write range. It can provide high-quality signal transmission in specific areas and is widely used in access .
mii fighter amiibo nfc tag
Designing an RFID antenna requires a methodical approach, starting with the selection of the operational frequency and appropriate antenna type, followed by detailed simulation and modeling to optimize its design.
rfid tag reading range
magnetic nfc tags
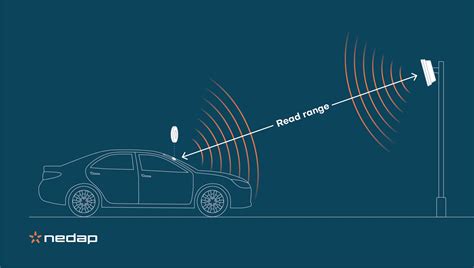
rfid tag read range chart
$14.99
rfid antenna read range|rfid longer read range