can nfc read uhf Ultra High Frequency (UHF) 856 MHz to 960 MHz; Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The . Vistaprint NFC Business Cards are designed and produced by Vistaprint, while Wave NFC Business Cards are produced by Wave, another prominent player in the NFC business card market. The key differences are in the design options, pricing, and additional features provided by each company.
0 · ultra high frequency nfc
1 · uhf rfid vs nfc
2 · stack overflow nfc
3 · rfid vs nfc
4 · nfc rfid reader
5 · nfc reader for android phone
6 · nfc for android phones
7 · long range rfid vs nfc
Tap NFC Keychain - Tap - Digital Business Card
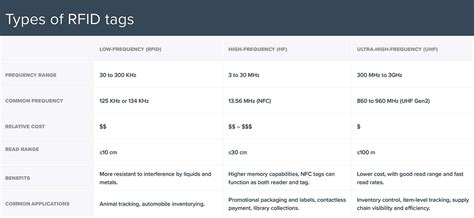
NFC enabled phones can ONLY read NFC and passive high frequency RFID (HF-RFID). These must be read at an extremely close range, . UHF RFID tags are considered the “supply chain frequency” because they’re generally lower priced than the other types, while still providing good read ranges and rates. Common applications include item-level tracking, .
UHF RFID: Moderate to high security, potential privacy concerns with a wider read range; NFC: High security, ideal for secure transactions or one-to-one communications; .Can NFC read signals at 13.56 MHz? Absolutely! NFC is intentionally designed to operate at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which aligns with high-frequency RFID technology. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) 856 MHz to 960 MHz; Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The . This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental .
ultra high frequency nfc
Sorry, Carl, that’s currently impossible, as there are no smartphones that contain an ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) reader. Some phones, such as Samsung ‘s Nexus S model, have a .
nfc card reader india
UHF: Can read up to hundreds of tags per second without a line of sight. NFC: this technology reads tags one by one as it requires close contact with the reader. It's ideal for contactless . NFC tags can be read via an NFC-compatible smartphone or an NFC RFID Reader. All you have to do is place the device close to the NFC tag, and it will automatically try to read .
Can NFC phones read RFID UHF tags ? No. Both the frequency and method of communication are quite different and NFC enabled phones are not able to read UHF tags. NFC enabled phones can ONLY read NFC and passive high frequency RFID (HF-RFID). These must be read at an extremely close range, typically a few centimeters. For longer range or any other type of RFID/active RFID, you must use an external reader for handling them with mobile devices. UHF RFID tags are considered the “supply chain frequency” because they’re generally lower priced than the other types, while still providing good read ranges and rates. Common applications include item-level tracking, retail inventory control and .
UHF RFID: Moderate to high security, potential privacy concerns with a wider read range; NFC: High security, ideal for secure transactions or one-to-one communications; Barcodes: Low security, can be easily replicated, or a bad actor can place a counterfeit QR or barcode overtop the existing barcodeCan NFC read signals at 13.56 MHz? Absolutely! NFC is intentionally designed to operate at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which aligns with high-frequency RFID technology. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) 856 MHz to 960 MHz; Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The standards and protocols of the NFC format is based on RFID standards outlined in ISO/IEC 14443, FeliCa, and the basis for parts of ISO/IEC 18092. This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility.
Sorry, Carl, that’s currently impossible, as there are no smartphones that contain an ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) reader. Some phones, such as Samsung ‘s Nexus S model, have a Near-Field Communication (NFC) reader in it. NFC is a short-range RFID technology that enables phones to read NFC tags.UHF: Can read up to hundreds of tags per second without a line of sight. NFC: this technology reads tags one by one as it requires close contact with the reader. It's ideal for contactless payments and quick data transfers. 3.Applications – How can we use them? NFC tags can be read via an NFC-compatible smartphone or an NFC RFID Reader. All you have to do is place the device close to the NFC tag, and it will automatically try to read it. 8.
Can NFC phones read RFID UHF tags ? No. Both the frequency and method of communication are quite different and NFC enabled phones are not able to read UHF tags. NFC enabled phones can ONLY read NFC and passive high frequency RFID (HF-RFID). These must be read at an extremely close range, typically a few centimeters. For longer range or any other type of RFID/active RFID, you must use an external reader for handling them with mobile devices.
UHF RFID tags are considered the “supply chain frequency” because they’re generally lower priced than the other types, while still providing good read ranges and rates. Common applications include item-level tracking, retail inventory control and . UHF RFID: Moderate to high security, potential privacy concerns with a wider read range; NFC: High security, ideal for secure transactions or one-to-one communications; Barcodes: Low security, can be easily replicated, or a bad actor can place a counterfeit QR or barcode overtop the existing barcodeCan NFC read signals at 13.56 MHz? Absolutely! NFC is intentionally designed to operate at a frequency of 13.56 MHz, which aligns with high-frequency RFID technology. Ultra High Frequency (UHF) 856 MHz to 960 MHz; Near-field communication devices operate at the same frequency (13.56 MHz) as HF RFID readers and tags. The standards and protocols of the NFC format is based on RFID standards outlined in ISO/IEC 14443, FeliCa, and the basis for parts of ISO/IEC 18092.
This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility. Sorry, Carl, that’s currently impossible, as there are no smartphones that contain an ultrahigh-frequency (UHF) reader. Some phones, such as Samsung ‘s Nexus S model, have a Near-Field Communication (NFC) reader in it. NFC is a short-range RFID technology that enables phones to read NFC tags.
UHF: Can read up to hundreds of tags per second without a line of sight. NFC: this technology reads tags one by one as it requires close contact with the reader. It's ideal for contactless payments and quick data transfers. 3.Applications – How can we use them? NFC tags can be read via an NFC-compatible smartphone or an NFC RFID Reader. All you have to do is place the device close to the NFC tag, and it will automatically try to read it. 8.
NFC Metal Business Cards - Customisable NFC Cards | Networking Solutions| Without V1CE Software | Elevate your networking with NFC (11) $ 40.60. FREE shipping Add to Favorites .
can nfc read uhf|stack overflow nfc