rf readings RF radiation has lower energy than some other types of non-ionizing radiation, like infrared and . $11.49
0 · what is rf radiation
1 · what does rf radiation mean cancer
2 · rf scans for cancer
3 · rf radiation for cancer patients
4 · rf exposure limits
5 · rf exposure frequency
6 · high emf readings
7 · high emf reading range
He was caught with 166,000 Czech koruna on his person, approximately $6500 .
High Radio Frequency Readings Summary: Radio frequency readings within living spaces above 1 mW/m² (milliWatt per square meter) are considered high. Alright, now let’s take a look at one of the most damaging and pervasive types of EMF radiation, radio frequency.RF radiation has lower energy than some other types of non-ionizing radiation, like infrared and . High Radio Frequency Readings Summary: Radio frequency readings within living spaces above 1 mW/m² (milliWatt per square meter) are considered high. Alright, now let’s take a look at one of the most damaging and pervasive types of EMF radiation, radio frequency.RF radiation has lower energy than some other types of non-ionizing radiation, like infrared and visible light, but it has higher energy than extremely low-frequency (ELF) radiation. If RF radiation is absorbed by the body in large enough amounts, it can produce heat.

What is non-ionizing radiation? How is radiofrequency energy used? How is radiofrequency radiation measured? What biological effects can be caused by RF energy? Can people be exposed to levels of radiofrequency radiation and microwaves that could be harmful? Can radiofrequency radiation cause cancer? In 1996, the FCC adopted updated guidelines for evaluating human exposure to RF fields from fixed transmitting antennas such as those used for cellular and PCS cell sites.Average µW/m² readings, as specified by the FCC, significantly under-report the levels of pulsed, data-modulated, RF microwave radiation exposures for two reasons —FCC Maintains Current RF Safety Rules: On November 27, 2019, the FCC voted to take a number of steps in its ongoing review of various rules pertaining to the implementation of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) requirements related to radiofrequency (RF) emissions from radio transmitters.
Microwave (MW) and radio frequency (RF) radiation is electromagnetic radiation that is lower in frequency and therefore longer in wavelength than infrared radiation. “Radiofrequency” is the name given to that section of the electromagnetic spectrum from frequencies of 300 kHz to 300 GHz. This presentation outlines the elements of a comprehensive RF Protection Program. These include the implementation of appropriate protective policies based on the potential for excessive RF exposures.Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency [1] range from around 20 kHz to around 300 GHz. Diagram 1: Electromagnetic Spectrum. Radio Spectrum and Wave Length. Table 2: Frequencies and Associated Usage. Cellular Communication Systems. Basically, two different systems exist for cellular phone communication in the US: Time Division Multiple Access TDMA. Code Division Multiple Access CDMS.
what is rf radiation
High Radio Frequency Readings Summary: Radio frequency readings within living spaces above 1 mW/m² (milliWatt per square meter) are considered high. Alright, now let’s take a look at one of the most damaging and pervasive types of EMF radiation, radio frequency.
RF radiation has lower energy than some other types of non-ionizing radiation, like infrared and visible light, but it has higher energy than extremely low-frequency (ELF) radiation. If RF radiation is absorbed by the body in large enough amounts, it can produce heat.What is non-ionizing radiation? How is radiofrequency energy used? How is radiofrequency radiation measured? What biological effects can be caused by RF energy? Can people be exposed to levels of radiofrequency radiation and microwaves that could be harmful? Can radiofrequency radiation cause cancer?
In 1996, the FCC adopted updated guidelines for evaluating human exposure to RF fields from fixed transmitting antennas such as those used for cellular and PCS cell sites.Average µW/m² readings, as specified by the FCC, significantly under-report the levels of pulsed, data-modulated, RF microwave radiation exposures for two reasons —FCC Maintains Current RF Safety Rules: On November 27, 2019, the FCC voted to take a number of steps in its ongoing review of various rules pertaining to the implementation of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) requirements related to radiofrequency (RF) emissions from radio transmitters. Microwave (MW) and radio frequency (RF) radiation is electromagnetic radiation that is lower in frequency and therefore longer in wavelength than infrared radiation. “Radiofrequency” is the name given to that section of the electromagnetic spectrum from frequencies of 300 kHz to 300 GHz.
what does rf radiation mean cancer
This presentation outlines the elements of a comprehensive RF Protection Program. These include the implementation of appropriate protective policies based on the potential for excessive RF exposures.
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency [1] range from around 20 kHz to around 300 GHz.
using phone as rfid tag
rf scans for cancer
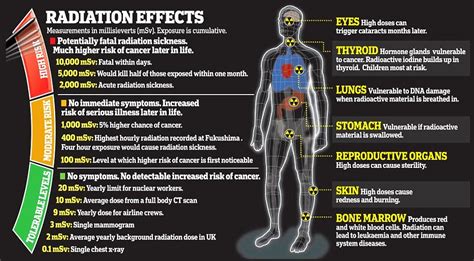
rf radiation for cancer patients
rf exposure limits
rf exposure frequency
Customised Metal NFC Business Card, Digi Business Card, Personalised Smart Visiting Card, .
rf readings|rf radiation for cancer patients