iot rfid sensor 6. Authors need to add the reference (Electronic sensor tags have the . Click LOAD TAG to load Amiibo data of the villager you want.; Click SAVE TAG to save chosen Amiibo data on to the tag of your choice. *Be aware that the NFC tags are NOT re-writable in this case, as official Nintendo Amiibos also lock in .
0 · rfid protocols in iot
1 · rfid iot devices
2 · rfid full form in iot
3 · radio frequency identification rfid technology
4 · iot rfid attendance system
5 · iot based smart attendance system
6 · iot based rfid attendance system
7 · explain rfid pillar of iot
Take fantastic photos with this unlocked Motorola Moto G7 smartphone. The 12.0-megapixel dual-lens camera with high-resolution zoom lets you capture clear, detailed subjects, and the 6.2-inch Full HD+ display provides immersive .
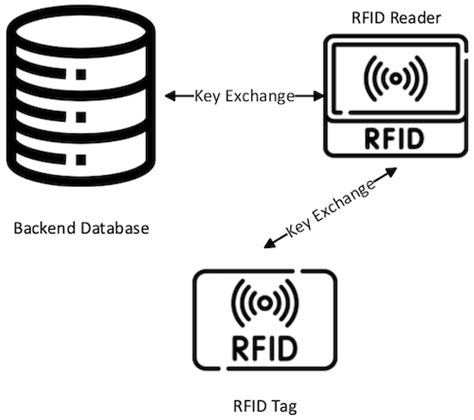
RFID sensors are a new paradigm for the internet of things (IoT). They have a .6. Authors need to add the reference (Electronic sensor tags have the .Action Date Notes Link; article xml file uploaded: 30 April 2021 12:57 CEST: .
Create a SciFeed alert for new publications. With following keywords. RFIDOrder Article Reprints. Journal: Sensors, 2021 Volume: 21 Number: 3138 Article: . Radio-Frequency IDentification (RFID) devices and sensors are among the main .
RFID sensors are a new paradigm for the internet of things (IoT). They have a limited cost and negligible maintenance, which make them appealing for numerous applicative scenarios such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and food. Radio-Frequency IDentification (RFID) devices and sensors are among the main innovations of the last years, with an enormous impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) physical communication layer as well as on logistics and robotics.
IoT is better for capturing real-time sensor data, while RFID is better suited for recording objects' proximity. IoT devices tend to be more complex and expensive, while RFID tags are generally optimized for low cost and simplicity. Radio frequency identification (RFID) and wireless sensors networks (WSNs) are two fundamental pillars that enable the Internet of Things (IoT). RFID systems are able to identify and track devices, whilst WSNs cooperate to gather and .RFID sensors are a new paradigm for the internet of things (IoT). They have a limited cost and negligible maintenance, which make them appealing for numerous applicative scenarios such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and food.
rfid protocols in iot
MIT researchers have designed photovoltaic-powered sensors on low-cost radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags that can transmit data, at greater distances, for years before needing replacement under sunlight and dimmer indoor lighting. In such a scenario the use of radiofrequency identification (RFID) is a very interesting and widespread solution to implement IoT systems or networks of distributed sensors. RFIDs are reasonably cheap, are provided with unique identifiers and can be equipped with a variety of sensing capabilities.In this chapter, a succinct review of RFID‐based sensors, considering both chip‐based and chipless‐based solutions, is carried out. A classification scheme of the main sensor types is reported, and the sensor working principle for each case is discussed. This article throws light on numerous chipless RFID sensors for IoT-based healthcare applications including their challenges and future directions. In addition to that, a comparison table of recent developments in the area of IoT-based healthcare is prepared.
RFID systems are becoming increasingly used to support internet of things deployments. Combining the technology with smart sensors and/or GPS technology enables sensor data including temperature, movement and location to be wirelessly transmitted. RFID sensors are a new paradigm for the internet of things (IoT). They have a limited cost and negligible maintenance, which make them appealing for numerous applicative scenarios such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and food.
Radio-Frequency IDentification (RFID) devices and sensors are among the main innovations of the last years, with an enormous impact on the Internet of Things (IoT) physical communication layer as well as on logistics and robotics.
IoT is better for capturing real-time sensor data, while RFID is better suited for recording objects' proximity. IoT devices tend to be more complex and expensive, while RFID tags are generally optimized for low cost and simplicity. Radio frequency identification (RFID) and wireless sensors networks (WSNs) are two fundamental pillars that enable the Internet of Things (IoT). RFID systems are able to identify and track devices, whilst WSNs cooperate to gather and .RFID sensors are a new paradigm for the internet of things (IoT). They have a limited cost and negligible maintenance, which make them appealing for numerous applicative scenarios such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, agriculture, and food.
MIT researchers have designed photovoltaic-powered sensors on low-cost radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags that can transmit data, at greater distances, for years before needing replacement under sunlight and dimmer indoor lighting. In such a scenario the use of radiofrequency identification (RFID) is a very interesting and widespread solution to implement IoT systems or networks of distributed sensors. RFIDs are reasonably cheap, are provided with unique identifiers and can be equipped with a variety of sensing capabilities.
In this chapter, a succinct review of RFID‐based sensors, considering both chip‐based and chipless‐based solutions, is carried out. A classification scheme of the main sensor types is reported, and the sensor working principle for each case is discussed. This article throws light on numerous chipless RFID sensors for IoT-based healthcare applications including their challenges and future directions. In addition to that, a comparison table of recent developments in the area of IoT-based healthcare is prepared.
rfid iot devices
contact smart card india
controlvault m6800 smart card
$14.50
iot rfid sensor|explain rfid pillar of iot